Strep throat is a bacterial infection of the throat and tonsils. The bacteria that cause strep throat are called group A Streptococcus (CDC 2024).
This same bacteria can also cause other infections, including scarlet fever, cellulitis and impetigo (Better Health Channel 2023).
Strep throat can affect anyone, but it is most common among school-aged children and teenagers between the ages of 5 and 15. Adults who are not exposed to children are unlikely to be infected, as are children younger than 3 (CDC 2024).
Strep A causes about one-third of sore throats in children but only 1 in 10 sore throats in adults (CDC 2024).

How is Strep Throat Transmitted?
Strep A bacteria are generally transmitted via respiratory droplets or direct contact with infected persons (VIC DoH 2024). The bacteria inhabit the nose and throat and spread to others through coughing and sneezing. It is possible for someone to be infected without displaying symptoms or appearing unwell (CDC 2024).
Strep A can be spread through:
- Breathing in respiratory droplets from coughs or sneezes
- Touching something with respiratory droplets on it
- Sharing drinks, plates etc. with someone who is sick
- Touching impetigo - sores on the skin caused by strep A bacteria.
(CDC 2024; Better Health Channel 2023)
Rarely, strep throat can be caught from contaminated food items, including:
- Milk and milk products
- Eggs.
(VIC DoH 2024)
Untreated individuals can be contagious for two to three weeks. However, after taking antibiotics, they are generally no longer contagious after 24 hours (Healthdirect 2023).
Risk Factors for Strep Throat
The following factors may increase the risk of Strep A infection:
- Being a school-aged child (between 5 and 15)
- Being a parent of a school-aged child
- Being an adult who is often in close contact with children
- Living in the same household as someone who has strep throat
- Spending time in a crowded facility (e.g. schools, daycare centres).
(CDC 2024)
Symptoms of Strep Throat
Symptoms may include:
- Sore throat that comes on quickly
- Pain when swallowing
- Red, swollen tonsils that may have visible white patches or streaks of pus
- Small red spots (petechiae) on the soft or hard palate
- Swollen, tender lymph nodes
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache
- Rash
- Fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting (particularly in children)
- Body aches.
(Mayo Clinic 2022; Healthdirect 2023)
Many of these symptoms are nonspecific to strep throat and could indicate a viral infection instead. A strep throat test should be conducted to determine the cause of symptoms (Mayo Clinic 2022).
The following symptoms may indicate a virus instead of strep throat:
- Cough
- Runny nose
- Hoarse voice
- Conjunctivitis.
(CDC 2024)
Complications of Strep Throat and Related Illnesses
Scarlet Fever
Strep A infection can also cause scarlet fever, which is a pink-red body rash with a sandpaper-like texture. It is mostly seen in children (NHS 2025).
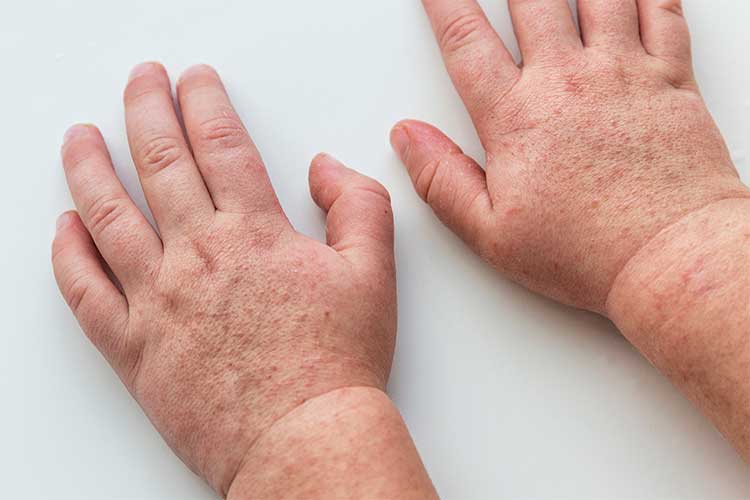
Impetigo
Impetigo refers to a skin rash caused by strep A bacteria, though it can also be caused by Staphylococcus aureus (golden staph). The rash causes blisters around the nose, mouth and legs and, in severe cases, can cause fever and swollen lymph nodes. The blisters are highly contagious (Better Health Channel 2023).
Rheumatic Fever
Rheumatic fever is a possible complication of strep A infection. It’s a serious inflammatory response to the strep A bacteria that may affect the heart, joints, nervous system and skin (CDC 2024; Mayo Clinic 2022).
Rheumatic fever can cause inflamed and painful joints, a rash, fever, breathlessness, chest pain and nervous system problems (such as involuntary twitching). It can also develop into permanent heart complications such as a heart murmur or enlarged heart (Better Health Channel 2011).
Diagnosing Strep Throat
To determine whether someone has strep throat, a laboratory test will need to be performed, as simply looking at the throat is inconclusive. The test involves a throat swab, which is then tested for strep A bacteria (Healthdirect 2023).

Treating Strep Throat
Treatment for strep throat requires a course of antibiotics. After the commencement of treatment, symptoms should begin to improve within one to two days and the person should no longer be contagious after 24 hours (CDC 2024; Healthdirect 2024).
Preventing the Spread of Strep Throat
The spread of Strep A can be prevented by:
- Regular handwashing
- Staying away from work, school, etc. when unwell
- Using tissues when coughing or sneezing and then disposing of them
- Avoiding sharing crockery, cups and utensils with other people
- Avoiding preparing food when unwell.
(Healthdirect 2023)
Test Your Knowledge
Question 1 of 3
True or false: Strep A accounts for most sore throats.
Topics
References
- Better Health Channel 2011, Rheumatic Fever, Better Health Channel, viewed 5 March 2025, https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/rheumatic-fever
- Better Health Channel 2023, Streptococcal Infection - Group A, Victoria State Government, viewed 5 March 2025, https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/streptococcal-infection-group-a
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2024, About Strep Throat, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, viewed 5 March 2025, https://www.cdc.gov/groupastrep/diseases-public/strep-throat.html
- Department of Health 2024, Streptococcal Disease (Group A Beta-haemolytic Streptococcus), Victoria State Government, viewed 5 March 2025, https://www.health.vic.gov.au/infectious-diseases/streptococcal-disease-group-a-beta-haemolytic-streptococcus
- Healthdirect 2023, Strep Throat, Healthdirect, viewed 5 March 2025, https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/strep-throat
- Mayo Clinic 2022, Strep Throat, Mayo Clinic, viewed 5 March 2025, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/strep-throat/symptoms-causes/syc-20350338
- National Health Service 2024, Scarlet Fever, NHS, viewed 5 March 2025, https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/scarlet-fever/

